Abstract
INTRODUCTION
TKIs are standard therapy for pts with CML, with therapy continued over several years and in many instances indefinitely. Cardiac effects of TKIs have been described, including prolongation of QTc and arterio-thrombotic events. Echocardiographic manifestations have been reported including a reduction in left ventricular ejection fraction (EF) and an increase in right atrial pressure (RAP) and right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP). However, no systematic description of these changes over the course of therapy has been presented. We retrospectively examined features and course of treatment of CML pts who had undergone echocardiogram during or following treatment with TKI therapy.
METHODS
We interrogated medical records for pts with CML who had undergone echocardiogram (ECHO). Pts were grouped by TKI and analyzed their age, race, sex, line of therapy, duration of therapy, and change of TKIs. Variables were analyzed using general linear model (for continuous variables), or chi-square test or Fisher's exact test (for categorical variables). T-test was used to compare EF, RVSP, and RAP measure before vs. during and during vs. after index TKI for patients with sequential ECHOs. To compare echocardiograph findings by TKI we used separate repeated measures ANOVAs for EF, RVSP, and RAP for patients with sequential ECHOs. All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS v9.4.
RESULTS
A total of 146 ECHOs were performed on 111 pts. 11 pts had ECHO before, during, and after TKI treatment, 17 pts had ECHO before and during TKI treatment, and 20 had ECHO during and after TKI. Their median age was 53 yrs (range, 15-83), and 53.1% were male. 95 (86%) were in CP at the time of TKI start; 71 (64%) were receiving their 1st TKI. TKIs used included imatinib in 53 (400 mg n=19, 800 mg n=34), dasatinib in 39, and nilotinib in 19. Among patients with 3 sequential ECHOs, 9 were on dasatinib, 1 on imatinib (400 mg), and 1 on nilotinib. Among patients with ECHOs before and during treatment, 13 were on dasatinib, 2 on imatinib (800 mg), and 2 on nilotinib, while among patients with ECHOs during and after treatment, 16 were on dasatinib, 1 on nilotinib, 1 on imatinib (800 mg), and 1 on imatinib (400 mg). Pt characteristics are presented in Table 1.
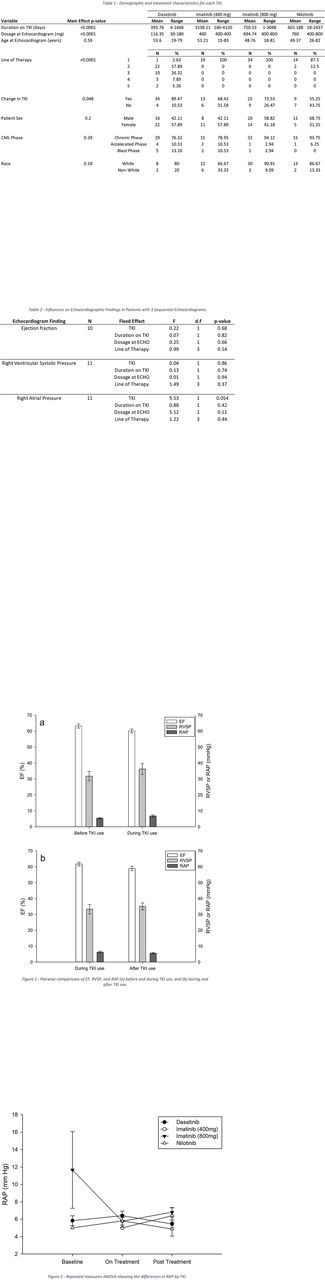
Considering all ECHOs in all pts, median EF was 62.5% before TKI, 60% during, and 60% after index TKI. Median RVSP was 30 mmHg before index TKI, 33 mmHg during, and 28 mmHg after TKI. Median RAP was stable at 5 mmHg throughout index TKI use. For patients with two sequential ECHOs, EF decreased significantly during TKI therapy (compared to baseline, difference=-3.1%, N=16, p=0.0186), and marginally after TKI (vs during, difference=-2.8%, N=20, p=0.091). There was a mild, non-statistically significant increase in RVSP from baseline to during TKI (difference=3.6 mmHg, N=16, p=0.30) and from during TKI to after TKI use (difference=1.9 mmHg, N=18, p=0.51). RAP did not differ from baseline to during TKI use (difference=1.1 mmHg, N=13, p=0.19), or during TKI to after TKI (difference=-0.71 mmHg, N=14, p=0.16). The results of these pairwise comparisons are presented in Figure 1. In repeated measures ANOVA of those patients with three sequential ECHOs, EF did not differ significantly among TKIs used (F=0.22, N=10, p=0.68), nor did RVSP (F=0.04, N=11, p=0.86). RAP was marginally different among TKIs used (F=9.53, N=11, p=0.054) (Figure 2). Full model results for these repeated measures ANOVAs are presented in Table 2.
CONCLUSION
Chronic administration of TKIs results in modest ECHO changes, particularly a slight decline in EF. There was also a modest increase in RAP with dasatinib and, to some extent, nilotinib but small sample size make these results preliminary. Still, monitoring of patients on TKIs with ECHOs at baseline and during therapy might be advisable.
Kantarjian: ARIAD: Research Funding; Delta-Fly Pharma: Research Funding; Amgen: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Bristol-Meyers Squibb: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding. Wierda: The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center: Employment; GSK/Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genzyme: Consultancy, Honoraria; Acerta: Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech/Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Juno: Research Funding; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Merck: Consultancy, Honoraria; Emergent: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Karyopharm: Research Funding; Kite: Research Funding; Sanofi: Consultancy, Honoraria. Jabbour: Bristol-Myers Squibb: Consultancy. Cortes: Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; ImmunoGen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Research Funding; ARIAD: Consultancy, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Sun Pharma: Research Funding; Teva: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.